Introduction
Reliability Growth Analysis (RGA) is an important part of reliability engineering, focused on improving system reliability during development and testing. By analyzing failure data, RGA helps engineers identify trends, estimate reliability parameters, and track improvements over time. These insights are essential for assessing the impact of design changes, guiding engineering decisions, and managing risks effectively.
The Crow-AMSAA Model
The Army Materiel Systems Analysis Activity model by Crow (Crow-AMSAA) takes failure behavior as a Non-Homogeneous Poisson Process (NHPP) governed by a power law, making the model particularly effective for systems undergoing reliability growth due to continuous improvements.
The Crow-AMSAA model is a statistical model that characterizes the relationship between the cumulative number of failures and cumulative time as the following:
where denotes the cumulative number of failures by time , is a scaling parameter, and is the shape parameter.
The shape parameter indicates whether the system’s reliability is improving or deteriorating.
- If < 1, then the system is improving (reliability is growing, the failure rate is decreasing).
- If = 1, then there is no change in reliability (the system is stable).
- If > 1, then reliability is worsening (the failure rate is increasing).
Example
To use the Crow-AMSAA model in ReliaGrowR, use the rga
function. This function takes a vector of failure times and a vector of
failure counts, and generates a plot of cumulative MTBF vs cumulative
time with the fitted model.
First, load the package:
Next, set up some time and failure data:
Then run the rga and plot the results:
result <- rga(times, failures)
plot(result, main = "Crow-AMSAA Model", xlab = "Cumulative Time", ylab = "Cumulative Failures")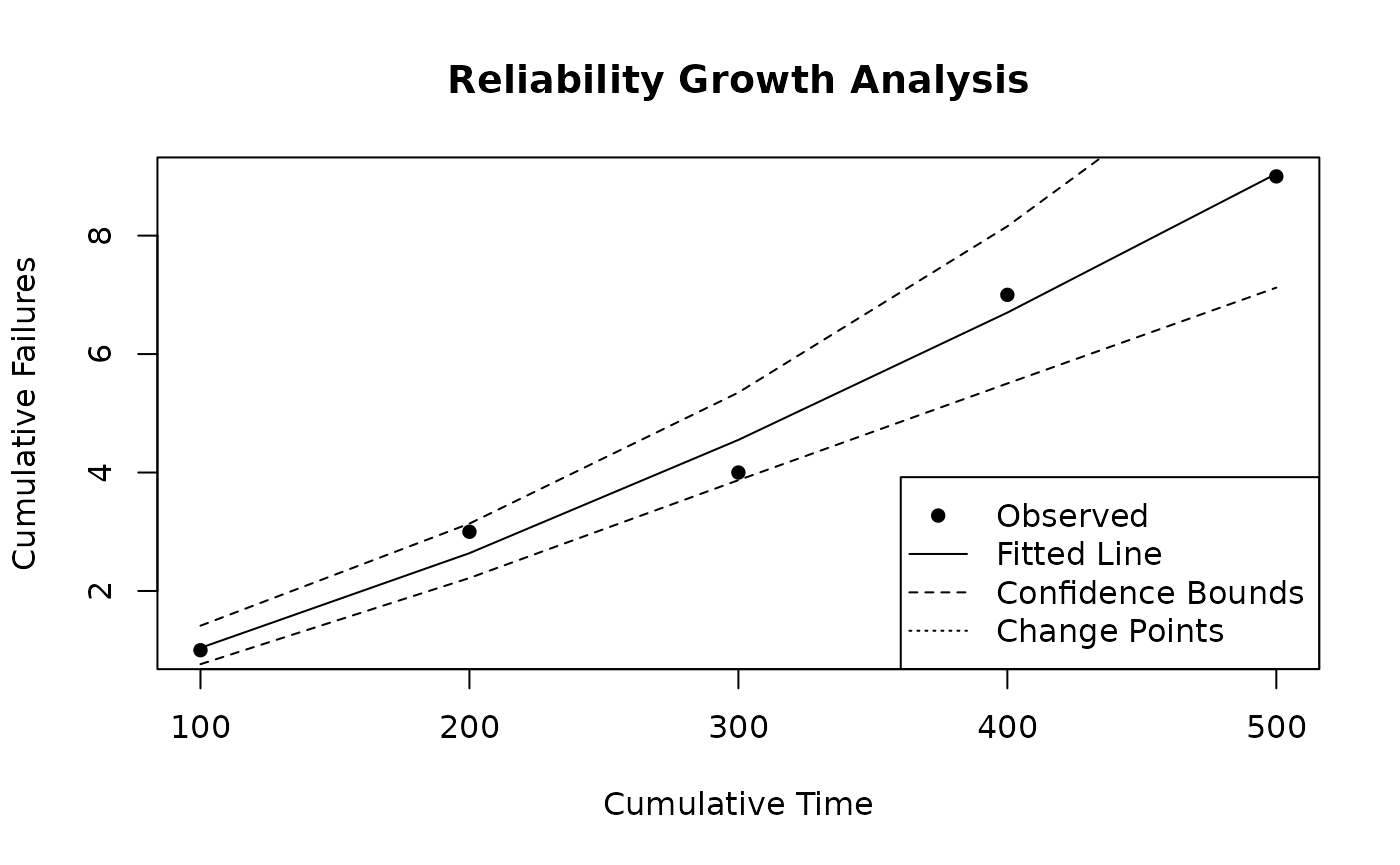
The plot shows the cumulative failures on the y-axis and cumulative time on the x-axis, with a fitted curve indicating the reliability growth trend.
The Piecewise NHPP Model
The Piecewise NHPP model is an extension of the standard NHPP model that includes different segments or phases of time that follow separate failure distributions. This model is particularly useful when a system experiences changes in failure behavior over different development phases, such as the initial, interim and final phases of a development process.
For a Piecewise NHPP model, the cumulative number of failures is modeled as a piecewise function, where each segment has its own parameters. Formally, for time t within phase i, the relationship between the cumulative number of failures and cumulative time is given by:
where is the cumulative number of failures by time in phase , is the scale parameter for phase , and is the shape parameter for phase .
Example
To use the Piecewise NHPP model in ReliaGrowR, first, set up some time and failure data and specify a breakpoint:
times <- c(25, 55, 97, 146, 201, 268, 341, 423, 513, 609, 710, 820, 940, 1072, 1217)
failures <- c(1, 1, 2, 4, 4, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 1, 1, 3, 3, 4)
breaks <- 500Then run the rga and plot the results:
result <- rga(times, failures, model_type = "Piecewise NHPP", breaks = c(breaks))
plot(result, main = "Piecewise NHPP Model", xlab = "Cumulative Time", ylab = "Cumulative Failures")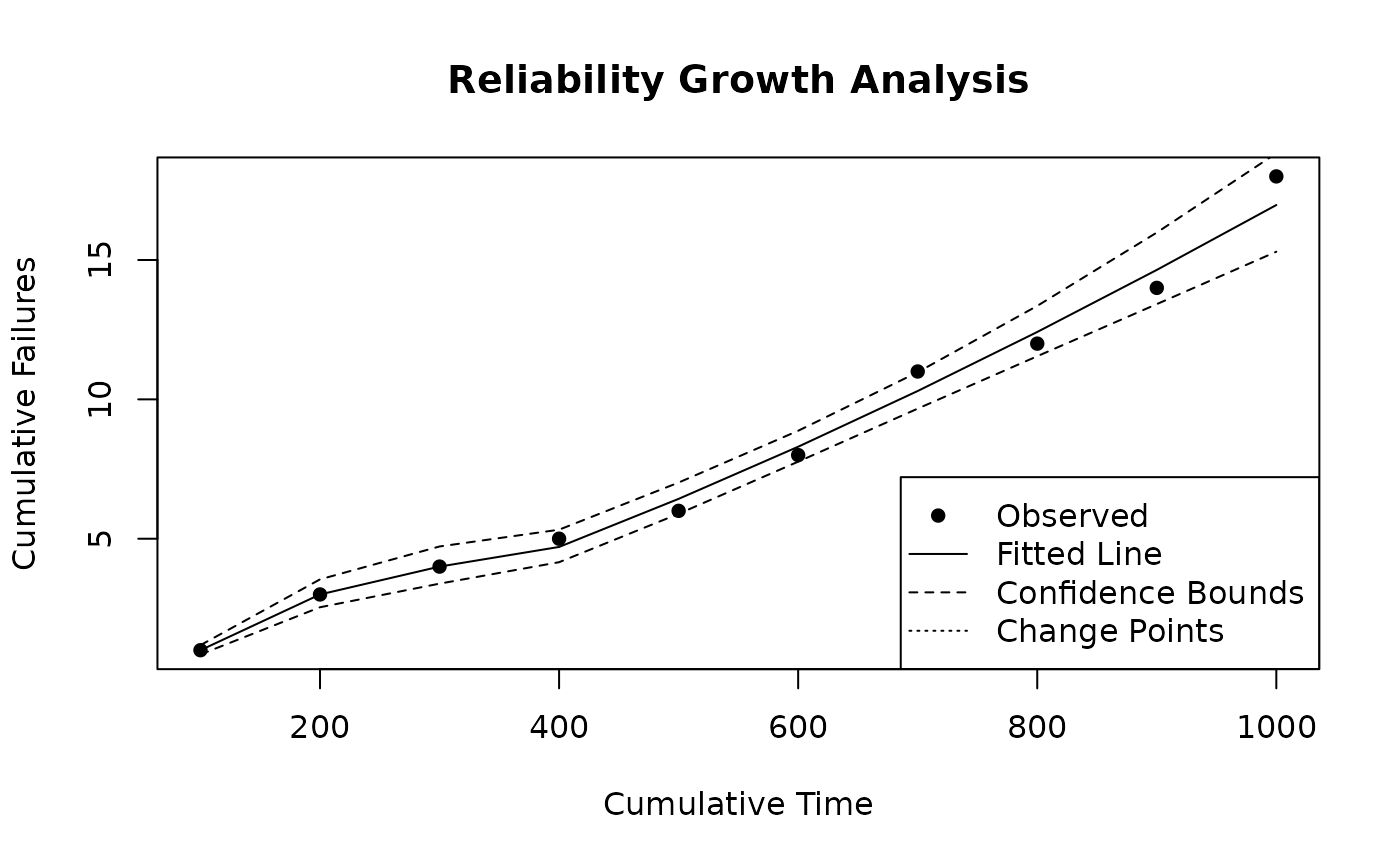
The Piecewise NHPP with Change Point Detection
The Piecewise NHPP with Change Point Detection is an advanced model to identify changes in failure behavior and model system reliability. This method builds on the Piecewise NHPP model by introducing the concept of change points, which represent the time when the underlying failure behavior changes. Detection of change points involves statistical techniques that analyze failure data to automatically identify when the behavior changes, allowing for a more precise segmentation of the model into different distributions.
Example
To use the Piecewise NHPP with Change Point Detection in ReliaGrowR,
use the rga function with the model type set to “Piecewise
NHPP” and breaks set to NULL. The function will automatically detect
change points based on the provided failure data. First, set up some
time and failure data:
times <- c(25, 55, 97, 146, 201, 268, 341, 423, 513, 609, 710, 820, 940, 1072, 1217)
failures <- c(1, 1, 2, 4, 4, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 1, 1, 3, 3, 4)Then run the rga and plot the results:
result <- rga(times, failures, model_type = "Piecewise NHPP")
plot(result, main = "Piecewise NHPP with Change Point Detection", xlab = "Cumulative Time", ylab = "Cumulative Failures")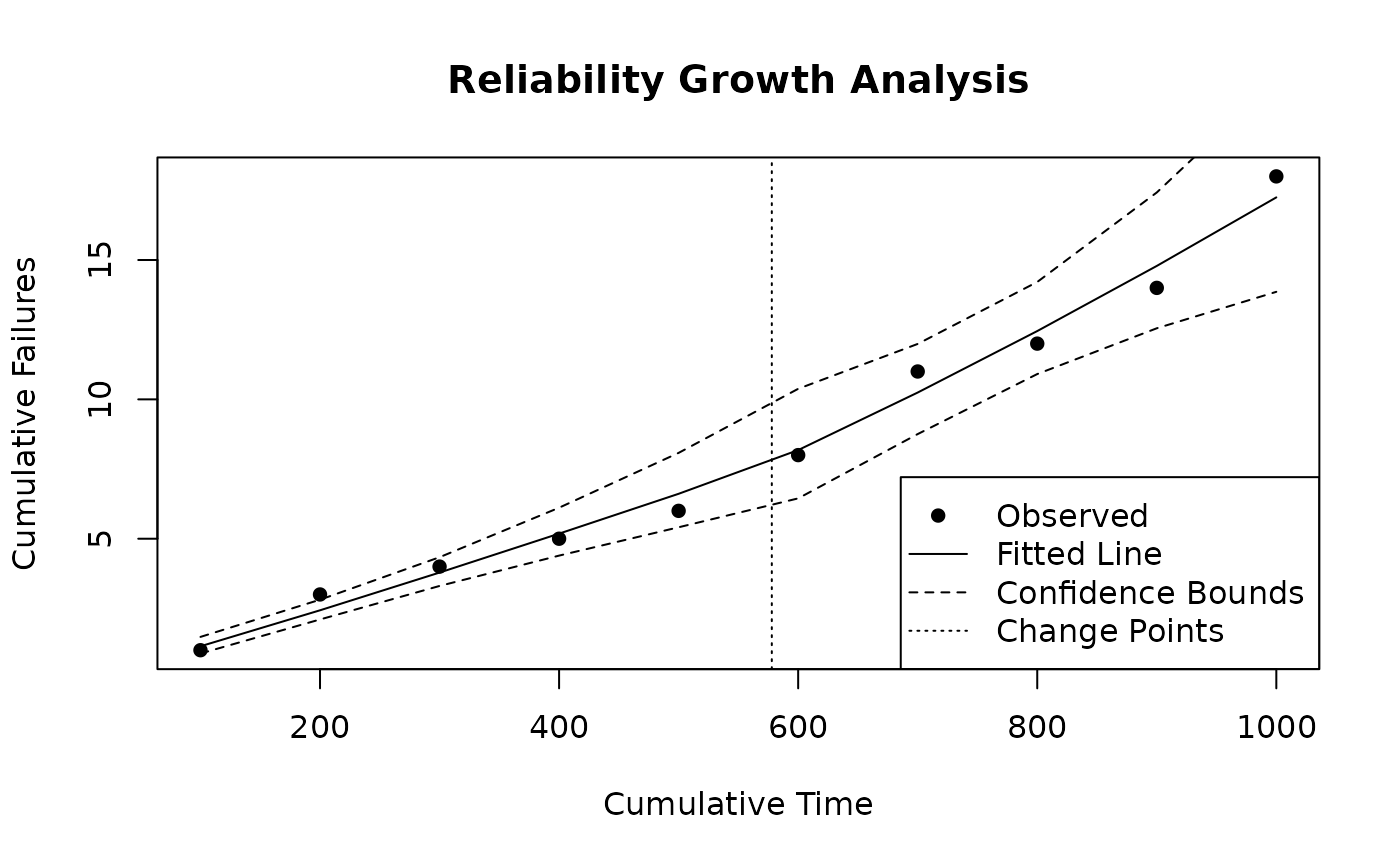
The Duane Model
The Duane model provides a simple and graphical way to observe and analyze whether failure rates are improving as changes are made to a product or system. The Duane Model is a log-log plot of the cumulative Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) vs cumulative time.
The slope of the line on the plot indicates the rate of reliability growth:
- A positive slope means that the system is improving (reliability is growing, the failure rate is decreasing).
- A zero slope means there is no change in reliability (the system is stable).
- A negative slope indicates that reliability is worsening (the failure rate is increasing).
To use the Duane Model in ReliaGrowR, use the duane_plot
function. This function takes a a vector of failure times and a vector
of failure counts, and generates a log-log plot of cumulative MTBF vs
cumulative time.
Example
First, set up some time and failure data:
Then fit the model and plot the results:
fit <- duane(times, failures)
plot(fit, main = "Duane Plot", xlab = "Cumulative Time", ylab = "Cumulative MTBF")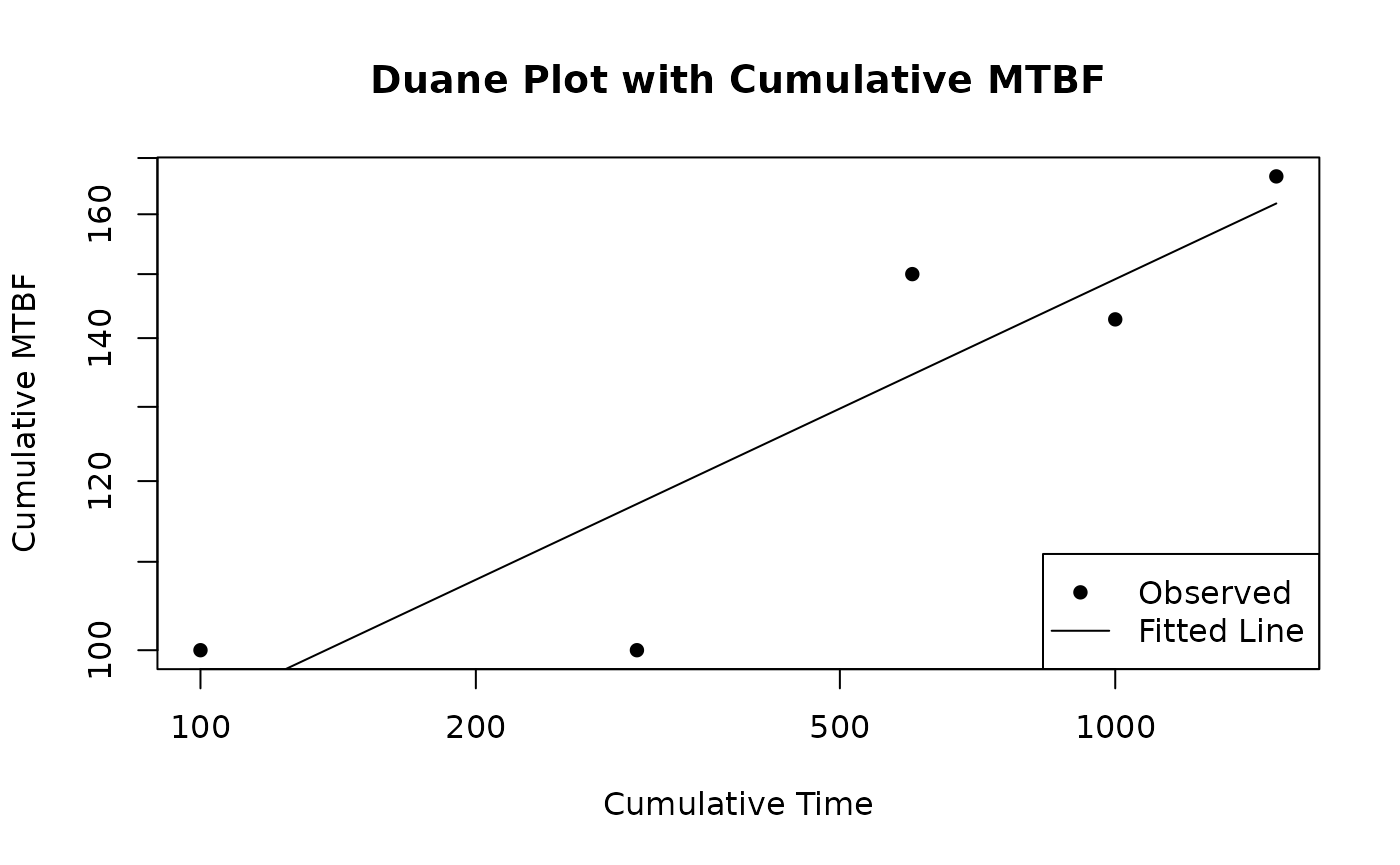
The plot shows the cumulative MTBF on the y-axis and cumulative time on the x-axis, with a fitted line indicating the reliability growth trend.
Goodness of Fit
Goodness of fit plots help assess how well a model matches the
observed data. Two key functions are qqplot.rga for Q-Q
plots and ppplot.rga for P-P plots. Both functions take an
rga object as input.
times <- c(50, 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, 600, 800, 1000)
failures <- c(1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8)
result <- rga(times, failures)
qqplot.rga(result)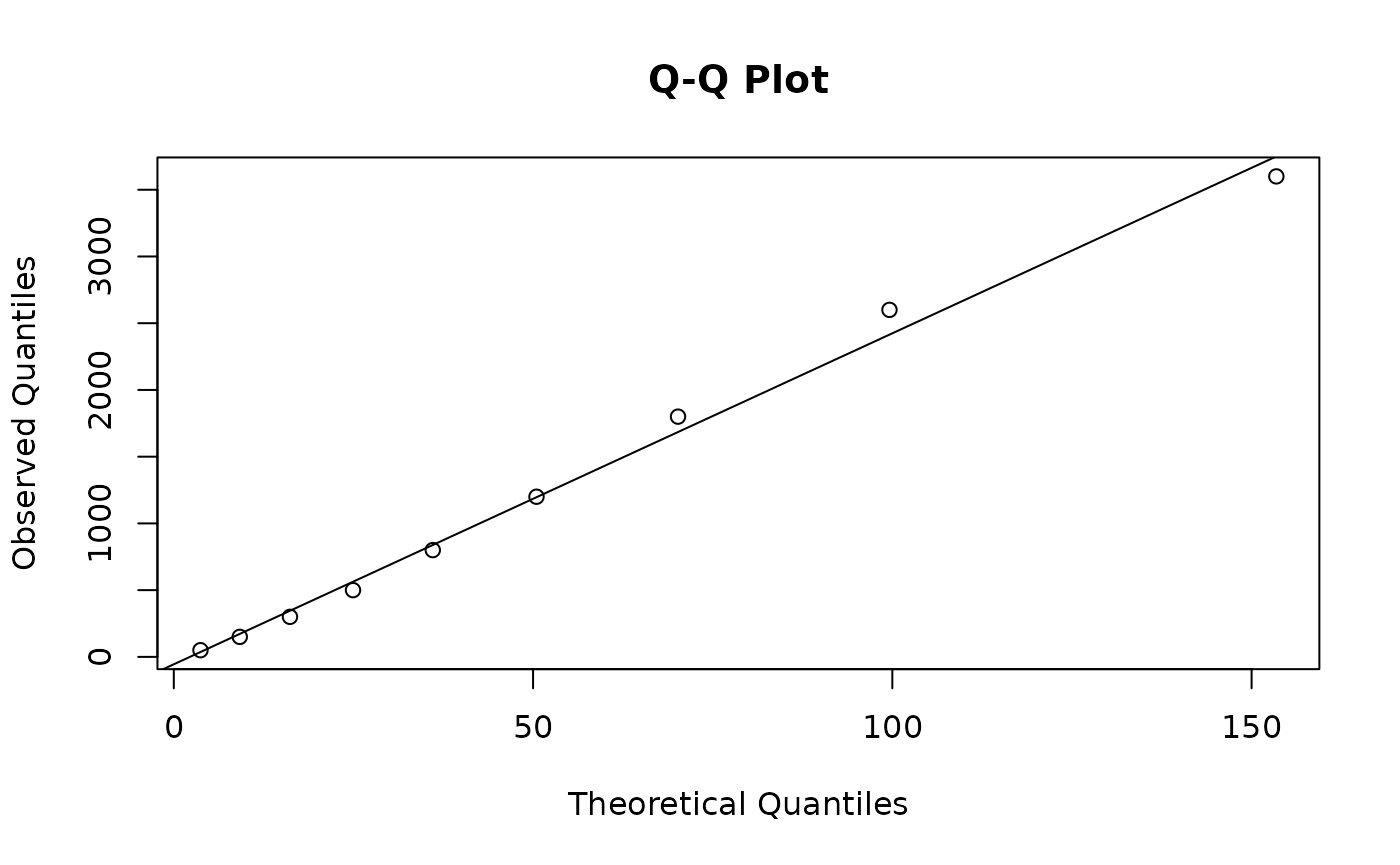
The qqplot.rga function produces a Q-Q plot that
compares the quantiles of the observed data with those of the fitted
model. A good fit is indicated when the points closely follow the
45-degree reference line.
Similarly, a P-P plot can be created with:
ppplot.rga(result)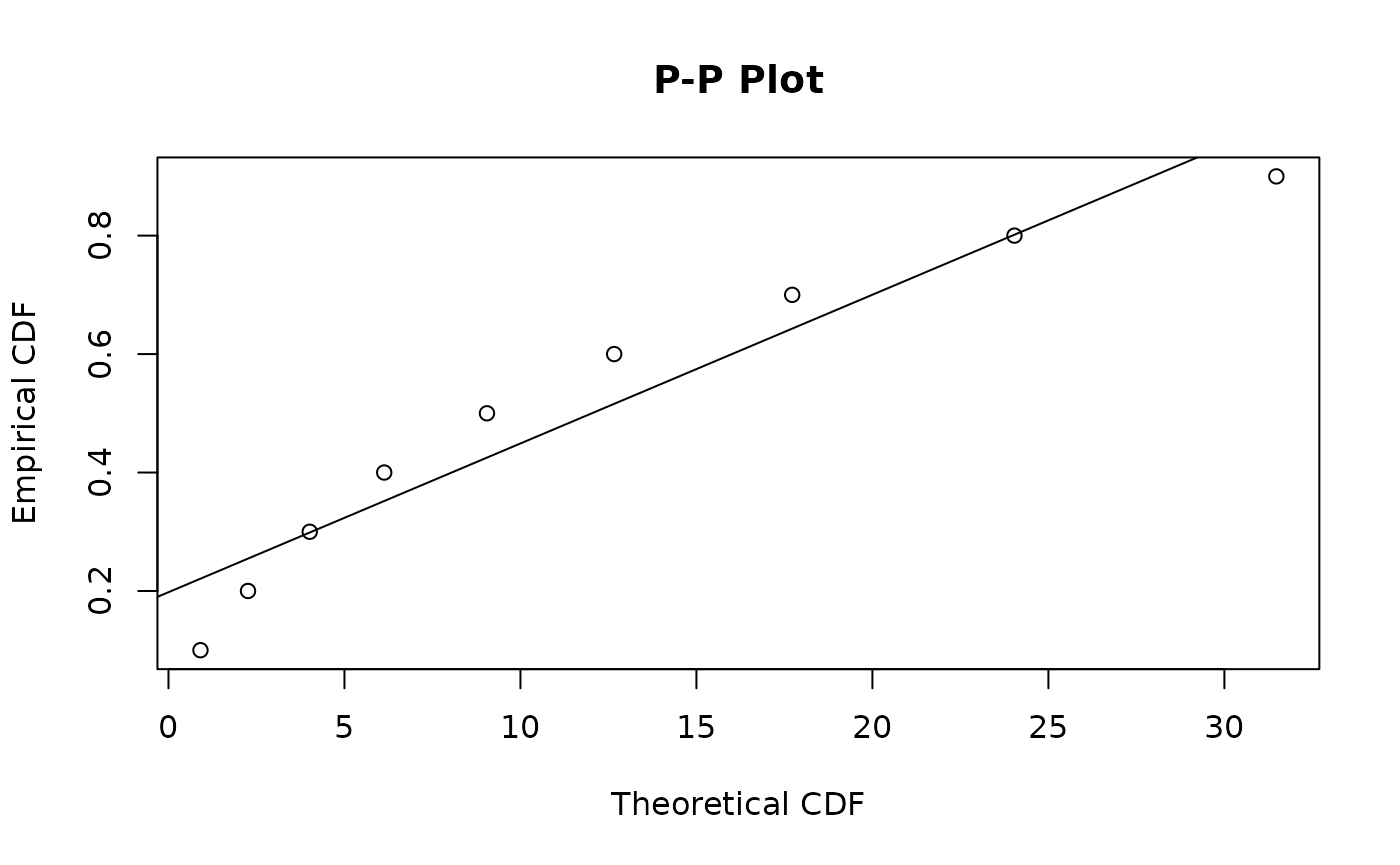
The ppplot.rga function compares the cumulative
probabilities of the observed data with those of the fitted model. As
with the Q-Q plot, a good fit is indicated when the points closely
follow the 45-degree line.
Data Conversion
Reliability data can be recorded in different formats, such as exact
failure times, right-censored times, or failure times grouped into
intervals. The weibull_to_rga utility function converts
data from the format used in the WeibullR package into the format
required for RGA analysis in ReliaGrowR. It accepts a vector of failure
times and optional vectors of right-censored (suspension) times and
interval-censored times, then returns a data frame with cumulative times
and failure counts suitable for use with the rga function.
For example, consider the following dataset with failure times, right-censored times, and interval-censored times:
failures <- c(100, 200, 200, 400)
suspensions <- c(250, 350, 450)
interval_starts <- c(150, 300)
interval_ends <- c(180, 320)The data can be converted using weibull_to_rga:
result <- weibull_to_rga(failures, suspensions, interval_starts, interval_ends)The resulting data frame contains cumulative times and failure
counts, which can then be passed directly to the rga
function for reliability growth analysis.
fit <- rga(result$CumulativeTime, result$Failures)
plot(fit, main = "RGA from Converted Data", xlab = "Cumulative Time", ylab = "Cumulative Failures")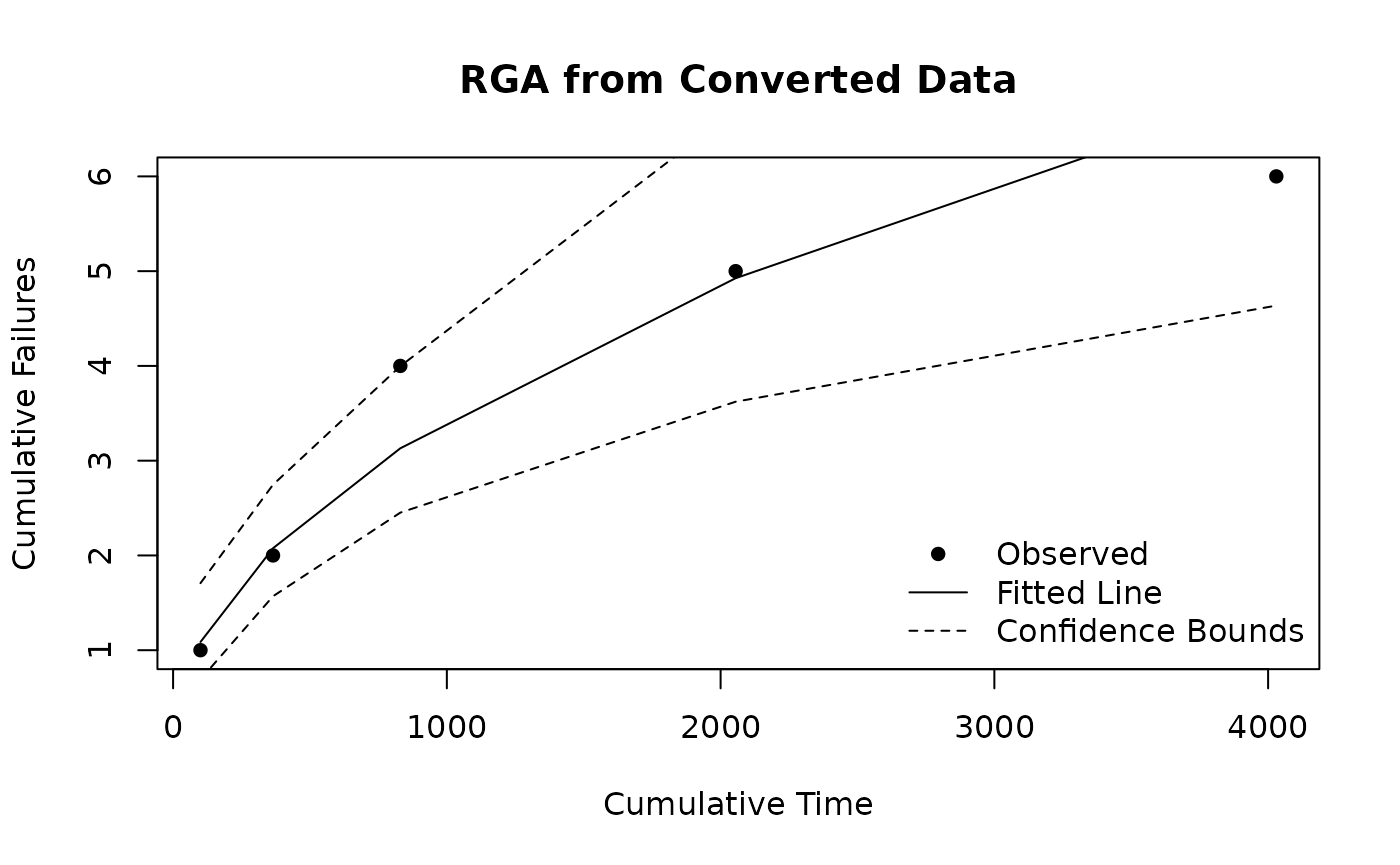
Summary
RGA provides a powerful statistical framework for tracking and predicting how a system’s reliability evolves throughout development. Models like Crow-AMSAA, Piecewise NHPP, and the Duane Model allow engineers and analysts to quantify improvements (or regressions) in reliability, understand system behavior across development phases, detect significant shifts in failure patterns, and guide design changes and process improvements.